Advanced Distribution Management System Test Bed
NLR's Advanced Distribution Management System Test Bed helps users evaluate existing and future advanced distributed management system (ADMS), distributed energy resource management system (DERMS), and other utility management system applications in a realistic laboratory environment.
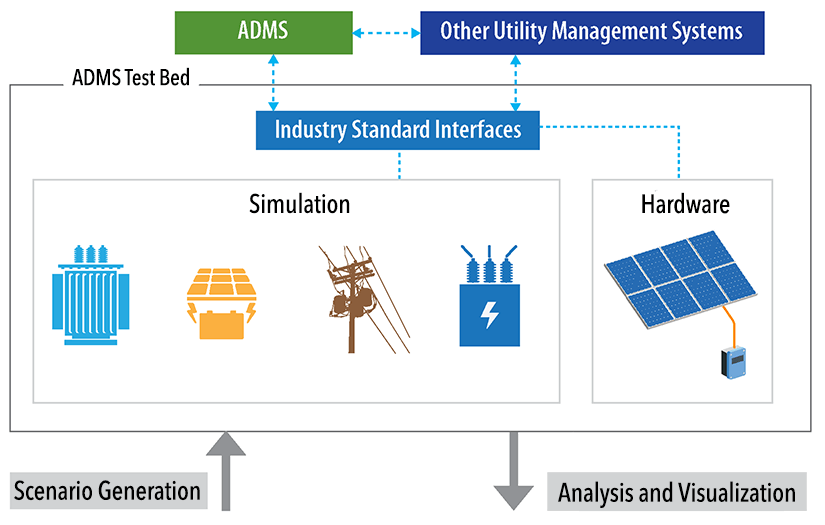
Overview diagram of the ADMS test bed.
The ADMS Test Bed is a national, vendor-neutral effort funded by the U.S. Department of Energy Office of Electricity’s Advanced Grid Research Program to accelerate industry development and the adoption of ADMS capabilities.
The ADMS Test Bed is an evaluation platform that consists of software simulations of large-scale distribution systems and field equipment integrated through hardware-in-the-loop techniques that realistically represent a power distribution system to a commercial or precommercial ADMS. The ADMS is interfaced to the test bed using industry standard communications protocols so it can be deployed as it would be in a utility environment. The test bed can integrate distribution system hardware in the Energy Systems Integration Facility for hardware-in-the-loop experiments and makes use of the facility’s advanced visualization capabilities, including 3D visualization. The test bed can also integrate simulations of end-use loads in buildings as well as home energy management system controllers with the distribution system simulation using the Hierarchical Engine for Large-scale Infrastructure Co-Simulation, an open-source, cyber-physical-energy co-simulation framework for electric power systems.
Capabilities
- Real-time co-simulation using Hierarchical Engine for Large-scale Infrastructure Co-Simulation
- Power hardware integration
- Controller hardware integration
- Industry-standard communications interfaces, including DNP3, MODBUS, and IEEE 2030.5
Projects
Renewable generation resources, energy storage systems, and flexible loads are increasingly integrated into the edges of electric grids. Distribution utilities are exploring ways to use DERs as non-wires alternatives to enhance system operations and incorporate the management of DERs as part of their strategies to offer affordable, reliable, secure, and resilient electricity services to their customers.
The rural cooperative Holy Cross Energy connected with NLR to outfit a new zero energy development with controllable DERs, including renewables. The development, named Basalt Vista, was modeled using the ADMS Test Bed, where researchers implemented and studied the performance of distributed control algorithms.
NLR and Holy Cross Energy—in collaboration with Survalent, the National Rural Electric Cooperative Association, and Heila Technologies—demonstrated a novel monitoring and control paradigm to manage a variety of assets at the grid edge. Holy Cross Energy incorporated the algorithms, and Basalt Vista is gaining national attention as a zero-energy success story. In this case study, the real-time optimal power flow algorithm—developed by NLRunder the Advanced Research Projects Agency–Energy Network Optimized Distributed Energy Systems program—was adopted and revised to develop a prototype DERMS that fits the needs of Holy Cross Energy’s system operations.
The project team evaluated the effectiveness of coordinating Survalent’s dynamic voltage regulation application on its ADMS platform with NLR's DERMS to achieve peak load reduction and reduce demand charges.
Read more about the partnership with Holy Cross.
Peak Demand Management and Voltage Regulation Using Coordinated Virtual Power Plant Controls, IEEE Access (2023)
Peak Load Management in Distribution Systems Using Legacy Utility Equipment and Distributed Energy Resources, IEEE Green Technology Conference (2021)
olorado's Xcel Energy is modernizing its electric grid operations in anticipation of continued growth in solar photovoltaic (PV) systems and electric vehicles. The ADMS Test Bed allows Xcel to quantify the impact that ADMS network-model quality will have on a Volt-VAR optimization (VVO) application. In this project, utility partner Xcel Energy—which was in the process of deploying an ADMS provided by Schneider Electric—planned to use the ADMS VVO application to reduce energy use and potentially the monthly bills for its customers.
The VVO application, when configured for energy conservation, aims to reduce energy use by flattening the voltage profile and reducing voltages across the feeder as much as possible while avoiding voltage exceedances. This is also known as conservation voltage reduction.
With the penetration of renewable generation continuing to increase in distribution systems, we can no longer assume that the voltage is lower the farther a point is located from the feeder head; therefore, the VVO application was configured for this research to use a network model and real-time measurements to optimize the set points of multiple legacy voltage control devices, including a load tap changer and four capacitor banks.
If a utility does not have a high level of confidence in the accuracy of the network model used by the ADMS, it could use more conservative constraints, keeping the voltages in the feeder higher to avoid undervoltage exceedances. This approach would result in reduced energy savings. Alternatively, a utility might invest in data remediation (specifically, data cleansing) to gain more confidence in the model so it can operate with less conservative constraints and potentially increase energy savings. Data remediation is an expensive and time-consuming process, and the results from this work helped Xcel Energy understand how much data remediation is required to achieve the desired result from its ADMS investment.
Model Quality and Measurement Density Impact on Volt/Volt Ampere Reactive Optimization Performance, Energies, Special Issue on Advances in Power and Energy Management for Distribution Systems With High Penetration of Distributed Energy Resources (2024)
Using an Advanced Distribution Management System Test Bed To Evaluate the Impact of Model Quality on Volt/VAR Optimization, IEEE Power and Energy Society Transmission and Distribution Conference and Exposition (2020)
Defining a Use Case for ADMS Testbed: Data Quality Requirements for ADMS Deployment, IEEE Conference on Innovative Smart Grid Technologies (2019)
In September 2020, the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission released Order 2222, which opens wholesale markets to small-capacity distributed energy resources, recognizing their potential in improving operational efficiency by providing bulk grid services. Therefore, a co-simulation capability that can connect transmission and distribution (T&D) simulations and evaluate the impacts of DER provision of bulk grid services is needed. We integrated NLR's ADMS Test Bed and Real Time Analytics for Bulk Grid capabilities to stand up a new integrated T&D co-simulation platform that incorporates T&D system simulators, DER aggregator/group strategies, and a co-simulation coordinator. Industry-standard communication protocols were employed to mimic real-world conditions. In collaboration with our partner, Xcel Energy, secondary frequency regulation was selected as the representative bulk grid service, and we simulated the responses of DERs to the frequency regulation signals for a solar-rich distribution feeder in Colorado, demonstrating how the T&D co-simulation setup is used to evaluate the contributions of DERs to minimize the bulk grid frequency deviation.
Integrated T&D Co-Simulation Platform for Demonstration of Bulk Grid Services Using Distributed Energy Resources, Energies (2024)
NLR evaluated the performance of a fault location, isolation, and restoration (FLISR) application of an ADMS on a Central Georgia Electric Membership Corporation electric distribution system with DERs using the ADMS Test Bed.
FLISR is one of the distribution automation applications that utilities are most interested in. It operates groups of switches on distribution feeders to improve the reliability of power delivery after localizing outages. FLISR is an essential function for enabling a self-healing electric grid, and it directly affects grid reliability and resilience.
The presence of DERs brings both new opportunities and challenges for FLISR applications. For instance, some DERs can work as backup generation sources and help energize local networks, so more switching options can be achieved with the coordination of FLISR operations; however, the existence of DERs also brings new challenges.
For this project, the team set up the ADMS test bed to use the FLISR application of the Survalent ADMS and a hardware-in-the-loop simulation of a feeder from Central Georgia Electric Membership Corporation, a cooperative electric utility.
Defining a Use Case for the ADMS Test Bed: Fault Location, Isolation, and Service Restoration With Distributed Energy Resources, IEEE Innovative Smart Grid Technologies (2021)
The ADMS Test Bed is being used to demonstrate a Federated Architecture for Secure and Transactive Distributed Energy Resource Management Solutions (FAST-DERMS) that is being developed to enable the provision of reliable, resilient, and secure distribution and transmission grid services through scalable aggregation and near-real-time management of utility-scale and small-scale DERs.
A flexible resource scheduler at the distribution utility level, which could be implemented on an ADMS, performs reliability-constrained economic dispatch of DERs, either directly or through a transactive market or DER aggregator. FAST-DERMS also allows for the seamless integration of any centralized distribution utility management system and a transmission energy management system at the independent system operator level. The project will end with a laboratory demonstration at NLR's ESIF using its ADMS Test Bed.
FAST-DERMS is being developed through funding provided by the Building Technologies Office and Office of Electricity’s Advanced Grid Research program through the Grid Modernization Laboratory Consortium. The project is led by NLR and supported by multiple partners, including Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory, Pacific Northwest National Laboratory, San Diego Gas & Electric, Southern Co., ComEd, and Oracle.
Shell, Spirae LLC, and NLR will partner to demonstrate and evaluate a distributed control architecture to manage and optimize grid-edge resources to meet multiple operating objectives. This project will show how utilities and grid-edge energy service providers can best support both end-customers and grid operations. Utility grid modeling and ADMS operations are typically conducted only up to end-use points like microgrids and aggregators, which limits the ability to model these end-users with sufficient resolution to make sound investment decisions on behalf of energy users. The joint project between Shell, Spirae LLC, and NLR will leverage the ADMS Test Bed to address this situation by co-simulating the grid and certain ADMS functions along with end-users and their distributed energy resources, energy management systems, and virtual power plants. Results of this proof-of-concept will show how utilities can model end-user systems to evaluate the simultaneous benefits to grid and customer operations.
Read more about the ADMS Test Bed project with Shell and Spirae LLC.
Electrical Grid Monitoring Inc., Israel Electric Corp., and NLR will partner to evaluate the performance impact of enhanced monitoring on power system restoration. This project with NLR will demonstrate an advanced grid monitoring system and its impact on grid operations. Currently, an ADMS acquires grid information from supervisory control and data acquisition systems that are installed in substations, but for grid distribution systems, the distance between substations is too distant to get actionable real-time data. This project will simulate a distribution network on the ADMS Test Bed to evaluate the impact of an enhanced monitoring solution developed by Electrical Grid Monitoring Inc. on fault location, isolation, and service restoration. Electrical Grid Monitoring Inc.’s monitoring augmentation aims to assist utility operators in obtaining better situational awareness, improving fault location precision, and reducing outage time.
Read more about this project on advanced grid monitoring systems.
Colorado Springs Utilities is interested in exploring how the electric grid can best accommodate increased demand from electric vehicles and charging stations and for this project, NLR will leverage software from Smarter Grid Solution, a wholly owned subsidiary of Mitsubishi Electric Power Products Inc., to investigate this question.
Springs Utilities will partner with NLR to test a section of its grid where a small-scale microgrid is planned for its Mesa Campus, which includes renewable energy sources such as solar, battery energy storage systems, and a public EV charging station. The hope is to determine the impacts additional energy demands, like EV charging stations, have on the microgrid and surrounding community and to test backup plans in case of power disruptions. To do this, Springs Utilities is teaming up with NLR to use Smarter Grid Solutions’ Strata Grid technology to test different scenarios to help Springs Utilities assess scenarios of high demand on the grid.
Read the announcement of this project: NLR Partners With Industry Leaders To Prove Out Grid Integration Solutions.
With approximately 7 million customers, Dominion Energy is interested in scale. The company is deploying Generac Grid Solution’s Concerto distributed energy resource management system across its service territory in Virginia and North Carolina to support EV owners and electric school buses, as well as customers with solar photovoltaics, battery storage, and other DER technologies. The utility also wants to simulate future scenarios to observe DERMS performance as the numbers of EVs and EV aggregators continue to grow.
The test bed will model a substation service area in the city of Suffolk, Virginia, and an accurate representation of its energy load. NLR experts will help Dominion Energy and Generac evaluate two grid control architectures for EV charging management using the Generac DERMS and multiple EV aggregators.
Read the announcement of this project: NLR Partners With Industry Leaders To Prove Out Grid Integration Solutions.
This project involved building a prototype distribution management system test bed that linked a General Electric Grid Solutions distribution management system to power hardware-in-the-loop testing.
This setup was used to evaluate smart-inverter operations and distribution management system integration of a mock utility distribution feeder and to compare the utility value of alternative volt/VAR schemes.
This project focused on opportunities to use smart inverters to support voltage regulation for power distribution systems and how to incorporate such capabilities in the software tools used by the utility to support grid operations.
Feeder Voltage Regulation With High-Penetration PV Using Advanced Inverters and a Distribution Management System: A Duke Energy Case Study, NLR Technical Report (2016)
Publications
Integration of Utility Distributed Energy Resource Management System and Aggregators for Evolving Distribution System Operators, Journal of Modern Power Systems and Clean Energy (2022)
Improving the Performance of Power-Hardware-in-the-Loop Co-Simulation With Quasi-Steady-State-Time-Series Models, IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics (2020)
Open-Source Framework for Data Storage and Visualization of Real-time Experiments, IEEE Kansas Power and Energy Conference (2020)
Testbed to Evaluate Advanced Distribution Management Systems for Modern Power Systems, IEEE Eurocon (2019)
Leveraging Standards to Create an Open Platform for the Development of Advanced Distribution Applications, IEEE Access (2018)
Design of the HELICS High-Performance Transmission-Distribution-Communication-Market Co-Simulation Framework, Workshop on Modeling and Simulation of Cyber-Physical Energy Systems (2017)
Developing Use Cases for the Evaluation of ADMS Applications to Accelerate Technology Adoption, IEEE Green Technologies Conference (2017)
View all NLR publications about the ADMS Test Bed.
Contact
Share
Last Updated Dec. 6, 2025
