All-Electric Vehicle Basics
An all-electric vehicle (EV) uses a battery to store the electrical energy that powers the motor.
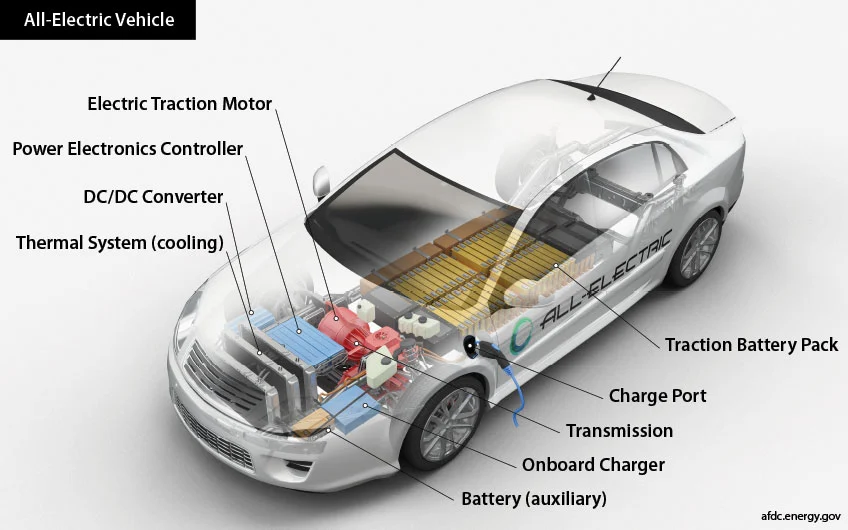
EV batteries are charged by plugging the vehicle into an electric power source. They are also equipped with regenerative braking systems to capture the kinetic energy normally lost during braking and store it in the battery.
EVs typically require less maintenance than conventional vehicles because the battery, motor, and associated electronics require little to no regular upkeep. Plus, electric vehicles experience less brake wear thanks to regenerative braking and have fewer moving parts and fluids to change relative to conventional vehicles.
Additional Resources
Transportation and Mobility Research
Electric Vehicle News and Feature Stories
Alternative Fuels Data Center: Electric Vehicles (U.S. Department of Energy)
Share
Last Updated Aug. 27, 2025
