ARIES Annual Report 2024
Advanced Research on Integrated Energy Systems (ARIES) is the U.S. Department of Energy's (DOE's) advanced research platform to validate our future integrated energy system with increasing integration of renewables, storage, and interactive loads at a size and scale that matters.

ARIES Vision
The Advanced Research on Integrated Energy Systems vision is to validate a broad range of future energy systems and grid modernization scenarios, helping stakeholders accelerate the implementation of energy technologies needed to meet the U.S Department of Energy's goals for a secure, affordable, and resilient energy system.
Addressing an Urgent National Need
ARIES accelerates the ability to research and validate innovative solutions for large-scale integrated renewable generation, storage, and increasing demand-side loads—essential technologies to realizing our national energy goals.
Developing an At-Scale Research, Development, and Deployment Platform
ARIES is DOE's advanced research platform for energy systems integration research, validation, and demonstration at a scale that reflects the real challenges faced by industry.
De-Risking Energy Systems
ARIES can replicate real-world scenarios of broad clean energy deployment, allowing users to safely demonstrate their best pathways to reaching local and national energy goals.
Distinguishing a National Asset
ARIES crosses multiple energy sectors, scales, and technologies. It joins together physical and virtual energy assets and enables national labs to combine their expertise and capabilities to address complex energy systems integration challenges.
ARIES Framework
Systems-level challenges drive the need for a research platform that can support integrated research, development, and demonstration at scale. ARIES focuses on solving three key challenges by addressing them through our strategic research areas: energy storage, future energy infrastructure, power electronics, cybersecurity, hybrid energy systems, and an emerging research area, industrial energy.
Key Challenges
Research Areas
Energy Storage to balance variable renewable generation and loads
Future energy infrastructure to adapt existing energy infrastructure for safety, monitoring, and controls
Power Electronics to control and integrate rapidly increasing electronics-based technologies
Cybersecurity to secure operations to prevent disruption, damage, and loss of functionality
Hybrid energy systems to achieve enhanced coordinated capabilities beyond isolated technologies
Industrial Energy to optimize energy solutions
2024 Impacts
In 2024, ARIES made significant progress to address the three challenges and advance the platform’s strategic research areas by:
2024 Numbers at a Glance
- ARPA-E
- Advanced Research Projects Agency-Energy
- BTO
- Building Technologies Office
- CESER
- Office of Cybersecurity, Energy Security, and Emergency Response
- DOE
- U.S. Department of Energy
- EERE
- Office of Energy Efficiency and Renewable Energy
- FECM
- Office of Fossil Energy and Carbon Management
- FEMP
- Federal Energy Management Program
- GTO
- Geothermal Technologies Office
- HFTO
- Hydrogen and Fuel Cell Technologies Office
- JOET
- Joint Office of Energy and Transportation
- NE
- Office of Nuclear Energy
- OCED
- Office of Clean Energy Demonstrations
- OCIO
- Office of the Chief Information Officer
- OE
- Office of Electricity
- OSP
- Office of Strategic Programs
- SC
- Office of Science
- SETO
- Solar Energy Technologies Office
- VTO
- Vehicle Technologies Office
- WETO
- Wind Energy Technologies Office
- WPTO
- Water Power Technologies Office
Learn more about the NREL facilities that make ARIES research possible:
Research Impacts
Integrating New Technologies

ARIES Launches Digital Twin Environment for Hybrid Geothermal Power Plants
Sponsor: GTO
Researchers are developing a geothermal digital-twin in a real-time simulation environment named Exergetic to study the performance of geothermal hybrid power plants, including their capability to provide grid services, flexibility, and resilience. Through the Advanced Research on Integrated Energy Systems (ARIES), the digital twin can be integrated with other power generation and energy storage technologies, as well as the electric grid, to evaluate the dynamic operation and to de-risk commercial deployment of geothermal hybrid systems.

ARIES Team Debuts 1-MW Capability for Evaluating Grid-Forming Inverters—The Key to 100% Clean Power
Sponsors: SETO and WETO
Started in 2022 by DOE and midway through a 5-year effort, the Universal Interoperability for Grid-Forming Inverters (UNIFI) Consortium continues to advance the development of grid-forming inverters with a multipronged, multi-institution approach. Among numerous accomplishments and publications, the team established an ARIES 1-megawatt (MW) demonstration platform to study grid-forming inverters, which debuted using inverters from several different manufacturers. The platform is open for vendors to validate operating modes and will help establish uniform requirements for interconnection and interoperability, a key to 100% clean power systems. Learn more about UNIFI's impact and outreach.

SuperLab Showcase: Connecting Five Geographically Dispersed Labs' Assets to Address the Challenges of Hybrid Energy Systems and Grid Complexity
Sponsors: OE, SC, FECM
The latest SuperLab experiment demonstrated how both current and future energy resources can seamlessly work together in a balanced energy system, representing power systems of today and the near future. The experiment combined 25 assets from 5 national laboratories—including renewable generation, storage, grid-edge resources, a gas turbine, and a nuclear small module reactor simulator—to determine how this plausible part-renewable system would fare during a major system fault. The demo was successful, furthering confidence in DOE's unique capability to run remote experiments centered at ARIES.
Impact of Gridge-Edge Devices

High-Power Vehicle Charging Hub Debuts With Open-Source Charge Management System
Sponsor: VTO
In the NREL-led, multi-lab project High-Power Electric Vehicle Charging Hub Integration Platform (eCHIP), researchers used new ARIES hardware to establish a hub for high-power electric vehicle (EV) charging and validate a first-of-its-kind technology with that hub: an open-source management system for optimizing charge time, cost, and energy sharing. The project connected DC chargers with battery energy storage, solar photovoltaics (PV), and building devices, and then showed that the resources can be orchestrated together for common charging and grid objectives. This work is part of the EVs@Scale Consortium and will enable a new generation of high-power charging experiments.

Flexible Charging Unifies the Grid and Transportation Sectors to Prepare for Electric Vehicles at Scale
Sponsor: VTO
To assess the charging demand of future EV adoption and determine the corresponding grid impacts, the NREL-led FUSE (Flexible charging to Unify the grid and transportation Sectors for Evs at scale) project team for the EVs@Scale Consortium is leveraging ARIES to conduct at-scale travel charging analyses and demonstrations of smart charge management and vehicle-grid integration strategies. This year, the team refined in-house controls, charging simulations, and a hardware test bed, which will then be used to demonstrate the real-world benefits of grid-transportation coordination.

ARIES Models and Simulates Homes Providing Flexibility to the Grid
Sponsor: BTO
Portland General Electric is interested in aggregating heating, ventilating, and air-conditioning systems, water heaters, battery energy storage, and EVs to supply flexibility to the grid in the DOE Connected Communities project SmartGrid Asset Load Management & Optimized Neighborhood (SALMON). To evaluate the controls that Portland General Electric will use for approximately 580 buildings, researchers modeled homes and developed a real-time simulation environment using ARIES. Next, they will deploy a commercial distributed energy resource management system at NREL with Portland General Electric's simulated network, showing how regular devices can amount to megawatts of grid flexibility.

ARIES Researchers Identify and Mitigate Cyber Risks of Clean Energy for Disadvantaged Communities
Sponsor: CESER
Researchers are working directly with communities and energy device manufacturers to understand and mitigate the cybersecurity threats affecting disadvantaged communities. In phase one of the project, the researchers gathered input and designed methodologies to address cybersecurity unknowns. They will apply their findings to the ARIES Cyber Range, allowing future projects to more realistically emulate risks for disadvantaged communities. The results will also be translated into a training course and analysis tool for utilities and other stakeholders.

Partners and Projects Queue Up for Megawatt Electrolysis, Storage, and Fuel Cell Capability
Sponsor: HFTO
The recently commissioned megawatt-scale ARIES hydrogen capability is now actively being used for research projects, including dynamic response and hybrid power plants. A flagship use case for the new capability saw the 1.25-MW electrolyzer connected to a solar array, wind turbines, and the campus grid controller, such that the electrolyzer produced hydrogen dynamically to match the excess renewable energy production. The demonstration of advanced grid coupling of hydrogen technologies, including long-duration energy storage and low-temperature electrolysis, is a top priority to ultimately meet DOE's Hydrogen Shot goals of reducing the levelized cost of hydrogen.

Fast-Fueling Protocol Validated With ARIES, Ready for Heavy-Duty Hydrogen Vehicles
Sponsor: HFTO
Researchers have used ARIES hydrogen fueling infrastructure to implement and validate an important fast-fueling protocol and develop a supporting heavy-duty hydrogen filling simulation model. The protocol is at the center of the heavy-duty hydrogen vehicle industry, and ARIES has made it possible for the first time to assess the protocol in real-world operations using industry-provided components. With industry partner Shell, researchers also demonstrated wireless communications between a vehicle and the station during fueling—another solution on the horizon for fast-fueling infrastructure.
Addressing Utility Deployment Challenges

Utility's Hybrid Battery-Hydrogen Microgrid De-Risked With ARIES
Sponsor: Energy Vault
NREL researchers partnered with Energy Vault to deploy a 3.45-MW battery inverter, 3/3.3-MWh battery energy storage system, and 1.6-MW fuel cell inverter, showing how these resources work in tandem to support microgrid operation during public safety power system shutdowns. The project team ran multiple at-scale experiments using ARIES medium voltage equipment, and after successful evaluations, this equipment was moved to Calistoga, California for field deployment. Results showed that the battery inverter and fuel cell inverter operated as designed during lab evaluation, giving Energy Vault and Pacific Gas and Electric Company (observers) the confidence to replace 10 MW of diesel generation with this unique hybrid battery and hydrogen asset.

Cybersecurity Researchers Use ARIES Cyber Range to Evaluate Cloud Data Feasibility for Complex Energy Systems Capability
Sponsor: OCIO
To help utilities feel confident about cloud data from a resilience and cybersecurity perspective, an ARIES team is evaluating cloud-based energy systems management in the project CloudZero. Within the ARIES Cyber Range, they have federated the cloud by installing multiple cloud environments in a single computing environment. This allows partners to try their use cases, with several already underway, including load forecasting, system failover/recovery, and bulk electric system reliability.
Learn more on YouTube about how the ARIES Cyber Range is being used to secure the cloud for energy systems.

Florida Utility's Solar Ambitions Drive ARIES Experiments in Grid Stability of Renewable Energy
Sponsor: SETO
With an expected solar PV capacity of 25 gigawatts (GW) by 2032, Florida Power & Light has good reason to reassess the electrical stability of its future power system, and ARIES offers the unique capabilities to do so. Researchers used ARIES to validate a common solar inverter model against its real electrical response at the microsecond timescale. This ensures that the utility is using a trustable model and will not encounter unexpected instabilities. Similar projects with industry partners are just getting underway to prevent instabilities by demonstrating diverse control interactions between renewable energy assets.
Capabilities and Buildout
ARIES comprises three pillars networked together to provide an interconnected and scalable research platform:
- The Energy Systems Integration Facility (ESIF) offers advanced research capabilities supporting experiments with up to hundreds of research devices, power levels up to 2 MW, and voltage levels up to 13.2 kilovolts (kV).
- The Flatirons Campus provides extensive hardware and simulation resources supporting experiments for thousands of research devices, power levels up to 20 MW, and voltage levels up to 34.5 kV.
- The Virtual Emulation Environment is a sophisticated digital platform that can incorporate physical assets from the ESIF and Flatirons Campus to emulate millions of devices at any utility power and voltage level and from local to national scales.
Map is for illustrative purposes to show which capability goes with each ARIES pillar. It is not a diagram of the capability itself.
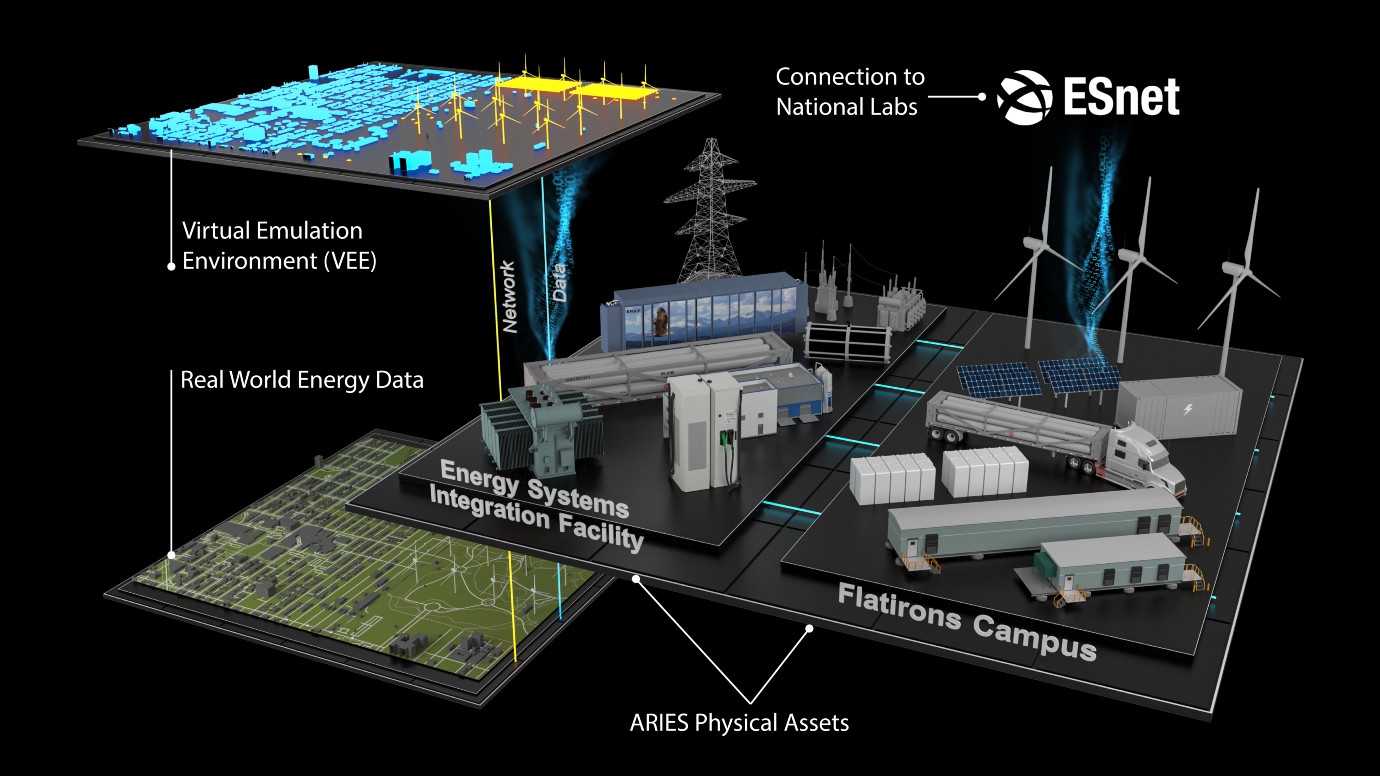
Select the dots to learn more about ARIES capabilities and buildouts.
Engagement and Outreach Highlights

Research Outcomes
Looking Ahead

Approaching 5 years of uniquely impactful research, ARIES is ramping up to take on more work than ever. Demand for our capabilities is growing—evidenced by the number and diversity of new projects—and those projects have an edge of urgency: They are about adapting to extreme weather, bolstering cybersecurity, and addressing the needs of energy intense industrial applications.
We are meeting increased demand with exactly what our partners need: higher power capacity, a wider variety of resources, more complex interconnections, precise models, and expert knowledge. With these ingredients, and the caliber of projects in the queue, it is truly exciting to see what's next. Some of the most exciting examples are our support for smaller communities.
Community Clean Energy Goals
Through the DOE Clean Energy to Communities (C2C) program, local groups get assistance with their clean energy goals, and ARIES is often central to discovering their approach. Two in-depth partnerships are evaluating renewable generation in remote Sitka, Alaska, and Molokai, Hawaii, while Colorado Springs, Colorado is leveraging ARIES for microgrid and EV integration. Another cohort selection is underway.
Microgrid Development in Underserved and Indigenous Areas
ARIES will support seven microgrid projects as part of an OE award to support microgrid solutions in underserved and indigenous communities. These projects will include workforce training, vendor-agnostic controllers, and software standardization—all important directions to strengthen resilience and access to replicable microgrid solutions in communities that are least equipped.
Threat-Informed Operational Collaboration and Collective Defense
The DOE Energy Threat Analysis Center (ETAC) convenes experts from the federal government, the U.S. energy sector, and the national laboratories to secure critical infrastructure against threats. Using the ARIES Cyber Range, NREL researchers will integrate hardware-in-the-loop assets with emulated reference architecture environments to strengthen the collective defense, response, and resilience of the U.S. energy sector. The Energy Threat Analysis Center leverages the range to quantify power system cybersecurity and resilience metrics across multilayered architectures surrounding cyber, physical, and human factors.
Rental Fleet Electrification Demo
ARIES will be used to emulate a fleet of electric rental cars in the project ATHENA ZEV, aims to help airports electrify their infrastructure. The demonstration will establish an integrated research environment to validate rental car charging scenarios with real hardware and emulated traffic flow along with the integration of solar and storage. Partners within the Athena project and beyond will be able to apply the setup and findings to their own zero-emissions efforts to prove out technology before it is deployed.

NREL works with organizations—large and small—to help stakeholders accelerate the implementation of energy technologies. You can partner with ARIES to de-risk technology solutions for a secure, affordable, and resilient future energy system. Watch for opportunities to work with us on the ARIES webpage or email us at ARIES@nrel.gov to discuss your project.
Advisory Committees
ARIES Steering Committee
The ARIES steering committee comprises DOE Office of Energy Efficiency and Renewable Energy (EERE) and NREL executive leadership. This committee meets biannually and has oversight of and responsibility for ARIES R&D management, research impacts, and financial and business practices.
Steering Committee Members
U.S. Department of Energy
- Alejandro Moreno
Associate Principal Deputy Assistant Secretary for the Office of Energy Efficiency and Renewable Energy - Michael Berube
Deputy Assistant Secretary for Sustainable Transportation and Fuels - Christy Cooper
Deputy Assistant Secretary for Operations - Becca Jones-Albertus
Deputy Assistant Secretary for Renewable Energy (Acting) - Marlys Kinsey
Director of the Golden Field Office (Acting) - Kevin Lynn
ARIES Lead and Director of Grid Modernization - Carolyn Snyder
Deputy Assistant Secretary for Buildings and Industry
ARIES External Advisory Board
The ARIES external advisory board provides an external perspective from industry, academia, and other government agencies/programs to NREL, DOE, and EERE on the research direction; research, development, and demonstration gaps that ARIES should address; and the development and deployment of the ARIES research platform.
- Chair: Gary Smyth
Executive Director, Global R&D Laboratories
General Motors (retired) - Jeffrey Baumgartner
Senior Advisor
Berkshire Hathaway Energy - Colton Ching
Senior Vice President, Planning and Technology
Hawaiian Electric Company - Elizabeth Endler
Chief Scientist
Shell - Lauren Faber O'Connor
Operating Partner
Lowercarbon Capital - Paula R. Glover
President
Alliance to Save Energy - Christopher Herbst
Vice President, Strategic Partnerships and Innovation
Eaton - Robert Horton
Vice President, Environmental Affairs
Dallas-Fort Worth Airport - Alice K. Jackson
Senior Vice President, System Strategy and Chief Planning Officer
Xcel Energy - Adrienne Lotto
Senior Vice President of Grid Security, Technical & Operations Services
American Public Power Association - Danielle W. Merfeld
Chief Technology Officer
QCells - Teresa R. Pohlman
Executive Director, Sustainability and Environmental Programs
U.S. Department of Homeland Security - Ronald M. Sega
Representative
U.S. Department of Defense - Timothy D. Unruh
Executive Director
National Association of Energy Service Companies - Evan Wolff
Partner
Crowell and Moring LLP
NREL ARIES Team
- Peter Green
Deputy Laboratory Director, Science and Technology - Johney Green
Associate Laboratory Director - Juan Torres
Associate Laboratory Director - Jennifer Kurtz
ARIES Research Director and Center Director - Jerry Davis
ESIF and ARIES Laboratory Program Manager - Rob Hovsapian
Senior ARIES Research Advisor - Matthew Thornton
Senior ARIES Research Advisor
Special thanks to:
Dane Christensen, Steve Hammond, Jordan Henry, Matt Keyser, Jennifer King, Daniel Laird, Barry Mather, Jibonananda Sanyal, and Josh Schaidle
Laboratory program managers, operations team, communications leads, executive assistants, project managers, partnerships development team, finance leads, and subject matter experts.

Share
