Subject Index - Grammar and Usage
- a and an
- affect and effect
- assure, ensure, and insure
- because and since
- capitalization
- compose and comprise
- criterion, datum, memorandum, phenomenon, and their plurals
- first-person pronouns
- hyphens, compound words, and unit modifiers
- inclusive language
- it's and its
- misplaced modifiers
- nonrestrictive phrases and clauses
- noun and adjective strings
- nouns
- over and under
- parallelism
- personal pronouns
- prefixes
- principal and principle
- race and ethnicity
- restrictive phrases and clauses
- spelling
- that and which
- time
- unit modifiers
- which and that
a and an
Use "a" before any acronym or word that begins with a consonant sound. Use "an" before any acronym or word that begins with a vowel sound. An acronym is pronounced as a word (for example, a HEPA filter); an initialism is pronounced as its letters (for example, an NGO). The first sound of the word or letters indicates whether to use "a" or "an." Examples: a light-water reactor, an LWR; a Human Resources Office memo, an HRO memo; a nongovernmental organization, an NGO; a National Renewable Energy Laboratory subcontract, an NREL subcontract.
affect and effect
"Affect" is usually a verb, and "effect" is usually a noun.
affect (verb):
effect (noun):
These words can be confusing because "affect" can sometimes be a noun (when it denotes an emotion), and "effect" can be a verb (when it means "to bring about").
assure, ensure, and insure
"Assure" means to make sure or give confidence. "Ensure" means to guarantee. "Insure" means to provide or obtain insurance.
Ensure the lid is fitted properly before starting the experiment.
The laboratory must insure the new equipment before it can be used.
because and since
"Because" indicates a cause-and-effect relationship. "Since" indicates a time relationship.
Since we began using the new procedures, there have been no more malfunctions.
capitalization
1. Proper Nouns
Capitalize proper names. These include the names of government programs, official projects, formal groups, organizations, companies, titles when they precede a name (use lowercase in titles that follow the name), specific geographic areas or features, and ethnic groups.
When referring to NREL, "National Renewable Energy Laboratory" is capitalized, but "the lab," "the laboratory," and "national laboratories" are not.
the Ethanol Project
the Human Resources Office
the U.S. Bureau of Mines
Solarex Corp.
President Carter
Christine Johnson, president and chief executive officer
the Southwest
Lake Powell
the Colorado River
African, Asian, Black, Caucasian, Hispanic, or Native Americans
One exception to this rule is companies and products with stylized lowercase or "camel cap" names (e.g., eBay, iPhone). In these cases, use the company’s or product’s preferred capitalization.
2. Figure Captions, Table Titles, and Section Headings
Figure captions: Capitalize only the first word and proper nouns in figure captions. No period needed (unless there are multiple full sentences).
Table titles and section headings: Capitalize the main words of table titles and headings and subheadings, including the second word in a hyphenated term (e.g., "PV Program Five-Year Plan"). No period needed.
Testing the 7.6-m Blades
Results for E. Coli
Development of Method To Detect Anomalies
Do not capitalize:
- Articles (e.g., "a," "an," and "the") unless they begin the title or heading
- Conjunctions of three or fewer letters (e.g., "and," "or," "nor," "yet," "so," and "but")
- Prepositions of three or fewer letters (e.g., "for," "of," "on," and "up").
Do capitalize:
- Conjunctions (e.g., "than") and prepositions of four or more letters (e.g., “from,” “with,” “above,” “after,” “down,” “inside,” “over,” and “into”)
- "To" as an infinitive (but lowercase as a preposition, e.g., “Scientists Travel to Chile To Engage Utilities”)
- Verbs, including "is" and "are."
For journal/conference submissions or other non-NREL publications, follow the style recommended by the professional society or publisher.
3. Titles
Capitalize titles when they precede the person's name. Lowercase titles and names of groups when they follow the name.
Mary Jones, the president of the company
John Smith, the chair of the committee
4. Trade Names
Capitalize trade or brand names, and include a trademark, copyright, or other symbol only when it's an Alliance-registered trademark. Include the symbol the first time you use the trade name in body text (not in a title, acronym list, or section header); thereafter, you may omit the symbol. Also use superscript for trademark symbols. See the trademark symbols entry for a list of Alliance trademarks.
5. Taxonomic Names
When writing about botanical and zoological divisions, capitalize the names of all divisions higher than species: genera, families, orders, classes, and phyla. Italicize genera, species, and varieties.
Clostridium thermocellum
Escherichia coli
After you first mention them (and spell them out), you can abbreviate most generic names followed by species names.
C. thermocellum
E. coli
See also captions, fiscal year, geographic regions, headings and subheadings, states and countries, and tables.
compose and comprise
"Composed of" is correct; "comprised of" is incorrect. See the examples below.
The parts constitute the whole.
The whole comprises its parts.
criterion, datum, memorandum, phenomenon, and their plurals
"Criterion" is a singular noun (one criterion), and "criteria" is the plural (two or more criteria). "Data" is the plural of "datum." The plural of "memorandum" can be either "memoranda" or "memorandums." "Phenomenon" is singular, and "phenomena" is plural.
first-person pronouns
See personal pronouns.
hyphens, compound words, and unit modifiers
Hyphenation rules can be intimidating, but remember that the ultimate goal is to provide as much clarity and consistency as possible. If you can’t find the proper hyphenation in this style guide, consult the AP Stylebook, followed by Merriam-Webster.
1. Verb Phrases: Verb, Noun, and Adjective Forms
Verb phrases that contain an adverb (e.g., build up, set up, start up, and break down) are usually written as two words. The noun and adjective forms of these words are usually one word, although there are exceptions.
The algae began to build up.
We helped with the setup.
To set up the experiment, begin with fresh samples.
The startup costs were more than we estimated.
The project is expected to start up next year
I think I'm having another breakdown.
It's time to break down the tent.
2. Compound Words Containing Prefixes and Suffixes
In most cases, you don't need a hyphen between prefixes or suffixes and the root words.
coauthor
cogeneration
coproduct
interregional
microgrid
midcareer
multidimensional
multiyear
nonlinear
nonspecialist
postdoctoral
prescreening
reevaluated
retroactive/proactive
semiconductor
subassembly
superposition
threefold, hundredfold
(also 100-fold)
ultrasonic
unbiased
underpredict
Exceptions:
Sometimes hyphens are needed when the root word begins with the same letter that the prefix ends in.
multi-integer
super-resolution
Use a hyphen between prefixes and proper nouns (but not common nouns) or dates whether they're used as nouns or modifiers.
mid-1990s
Use two hyphens when adding a prefix to a word that already contains a prefix, even when there is no hyphen after the prefix in the original word.
Finally, these prefixes usually require a hyphen: "ex," "self," and "quasi."
3. Unit Modifiers With and Without Hyphens
Use a hyphen to indicate that words have been combined into a unit modifier, which is a descriptive expression composed of two or more words that form one new meaning. For example, in the term "flat-plate collector," "flat-plate" is the unit modifier. Here are some examples of unit modifiers that usually include hyphens:
last-minute addition
high-temperature process
fatigue-induced wear
nine-story building
cost-effective solution
To see how adding the hyphen can prevent confusion, consider these examples:
The scientists tested a new defect-causing gas.
In the first example, the scientists might seem to have tested a defect; in the second example, it's clear that they tested a gas.
You don't need a hyphen in common unit modifiers that are not ambiguous or confusing.
solar radiation resource
solar thermal electric systems
Don't use a hyphen when both words of a unit modifier are capitalized.
Pacific Ocean exploration
World Cup qualifier
Leave out the hyphens if you rewrite a sentence so the words in the unit modifier come after the noun they describe
We purchased state-of-the-art lab equipment.
We purchased lab equipment that reflects the state of the art.
They made some last-minute adjustments.
They made some adjustments at the last minute.
Don't use a hyphen with a unit modifier containing an adverb ending in "-ly."
frequently missed deadlines
commonly seen mistakes
Don’t use a hyphen with two-word Latin phrases when the phrases are used as modifiers.
candidates for in situ testing at wind farms
at the atomistic scale, ab initio models provide detailed descriptions
When you use numbers in unit modifiers, retain all the necessary hyphens. However, do not use a hyphen to join a number and words such as “million” or “billion.”
13-cm-wide substrate
$4 million prize
Or rewrite the sentence to omit the hyphens.
a substrate that is 13 cm wide
Use suspended hyphens when your compound modifier is interrupted by another word, such as part of a list.
5- and 10-m blades
Suspended hyphens can also be used for different prefixes on the same root word (micro- and mesoscale), but the preferred style is to write out each word fully (microscale and mesoscale). Use your best judgment, considering both the context and audience.
4. Common Hyphenated Terms
Certain words and phrases are always hyphenated, regardless of context. Examples include:
decision-making (but decision maker)
de-risk
problem-solving
techno-economic
inclusive language
The way we communicate reflects our priorities as a laboratory; using inclusive language is respectful and promotes equity. Following are brief discussions of common topics related to inclusivity—please use this as a starting point as you examine the words that you use and their impact.
Race
The race and ethnicity entry covers capitalization, hyphenation, and word choice. Beyond that, be mindful of terms and phrases with racist histories—these can be prevalent in both scientific writing and everyday language.
“whitelisting/blacklisting,” (replace with “allow list/deny list” or similar)
“brown bag” (replace with “lunch and learn”)
All written, audio, and visual products at NREL must comply with Section 508, which allows assistive technology (e.g., a screen reader) to relay information to a person. Visit the 508 compliance entry to learn more about captions, alt text, and clear navigation of PDFs, webpages, and more.
Also, take care to avoid using unintentionally ableist language. Examples like “blind to,” “fall on deaf ears,” “crippled by,” and so on imply that people with these disabilities are ignorant or helpless. Instead, reword your sentences to be specific and clear with what you are trying to convey.
Gender
Whenever possible, use words that apply to any gender, such as “moderator” rather than “chairman” or “manufactured” rather than “man-made.” In addition, honor the pronouns that a person has chosen to describe themself. Note that the nongendered “they” is appropriate in reference to a single person or a group of people; further, “they” is preferred over “he/she,” which often feels cumbersome in text and is less comprehensive.
The AP Stylebook has entries on inclusive storytelling and gender-neutral language.
Sexuality, Age, Religion, and Socioeconomic Status
Be mindful in your writing to not assume victimhood or inadvertently apply stereotypes. For example, rather than “poverty-stricken,” use “low-income.” Instead of “elderly,” use “older adults.” Avoid “the” descriptors (e.g., “the homeless,” “the poor”) because they are usually dehumanizing. Also, when considering identity-based descriptors such as sexuality, age, or religion, consider whether the descriptor is appropriate to include. If it is not relevant to the story, there are often more neutral ways of describing a person or group.
Inclusiveness Check
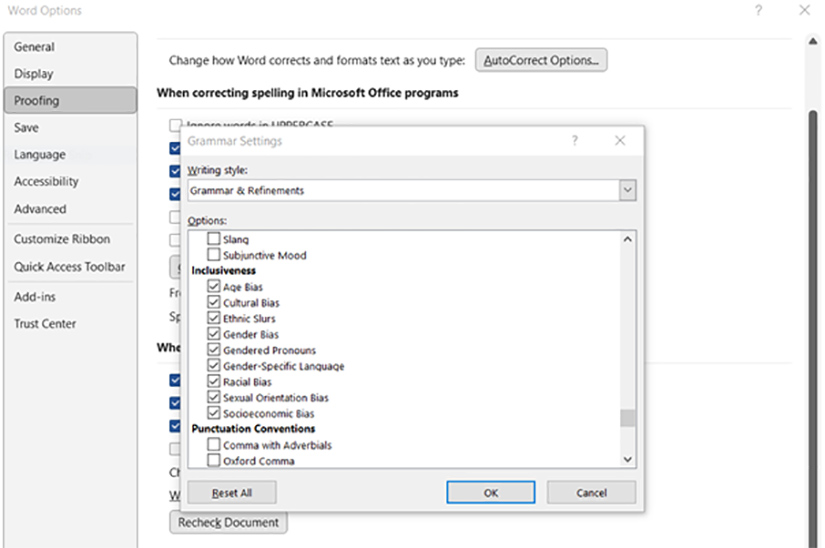
Microsoft Word offers an inclusiveness check as part of its proofing options. However, similar to how spell-checkers do not replace review by an editor, this inclusiveness check does not replace common sense regarding eliminating biases and promoting respect. To turn on this inclusiveness check, go to File > Options > Proofing, click on the “Settings” button next to “Writing Style,” and check all the boxes under the “Inclusiveness” heading.
Other Resources
There are many resources available about inclusive language and promoting diversity and equity in your writing. Following are a few that may be helpful:
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 2022. “Preferred Terms for Select Population Groups & Communities.” https://www.cdc.gov/healthcommunication/Preferred_Terms.html.
Ferguson, Jackie, Kaela Kovach-Galton, and Roxanne Bellamy. 2020. Say This, Not That: Activating Workplace Diversity Through Inclusive Language Practice. The Diversity Movement. https://thediversitymovement.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/11/WW-SayThis-whitepaper_201116-F.pdf.
Google. 2021. “Striving for a more inclusive workplace? Start by examining your language.” https://www.thinkwithgoogle.com/intl/en-ssa/future-of-marketing/management-and-culture/diversity-and-inclusion/diverse-workplace-inclusive-language/.
Inclusive Naming Initiative. 2023. “Frequently Asked Questions.” https://inclusivenaming.org/faqs/.
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory. 2022. Pronouns Matter Everyday. LLNL-BR-831843. https://www.llnl.gov/sites/www/files/2022-03/Pronouns_Matter_%2020220308.pdf.
Linguistic Society of America. 2016. “Guidelines for Inclusive Language.” https://www.linguisticsociety.org/resource/guidelines-inclusive-language.
Questions can be directed to the Editorial Board or the Office of Diversity and Inclusion.
it's and its
Even though "it's" has an apostrophe, it isn't a possessive pronoun. "It's" is a contraction, a short form of two words, like "isn't." "It's" always means "it is." "Its" is the possessive form of "it." Like "his," "hers," and "ours," the possessive "its" never needs an apostrophe.
misplaced modifiers
Modifiers in the wrong place can make a sentence confusing.
In this example, it isn't clear who or what identified the correct material. This might be better: After identifying the correct material, we conducted the 5-minute test procedure.
What, or who, was lost—the manuscript, the woman, or the reader? Try to keep modifiers as close as possible to the people and things they describe. Strunk and White, authors of The Elements of Style, say this: "Modifiers should come, if possible, next to the word they modify." This is especially true for sentences containing introductory prepositional phrases or clauses followed by a comma.
nonrestrictive phrases and clauses
A nonrestrictive phrase or clause is one that adds information but is not essential to the meaning of the sentence.
The passive solar features, which were suggested by NREL staff, reduced the agency's energy bills by 30%.
Nonrestrictive or nonessential phrases and clauses are enclosed between two commas when the phrase or clause is within a sentence, and they usually begin with "which" rather than "that." See also restrictive phrases and clauses and which and that.
noun and adjective strings
Try not to string too many nouns and adjectives together in a sentence. An "agency personnel communications interface display" could also be called a "display of the communications of the agency's personnel." Better yet, it could just be called the "staff bulletin board."
nouns
To give your writing more flow and vigor, try changing some of the nouns (especially those ending in -tion and -ment) to verbs (e.g., determine, complete, accomplish, achieve, measure, convert, characterize, combine) and other parts of speech. Doing this will move your readers along more quickly and make it easier for them to understand your text. In these examples, we changed some of the nouns in the first sentences to verbs and other parts of speech.
The tree stems contracted rapidly.
The frequent result of this process is the combination of the molecules.
This process frequently causes the molecules to combine.
The application of fertilizer has the result of stimulation of the yield.
Applying fertilizer stimulates the yield.
Which sentences were easiest to read and understand?
over and under
In cases involving quantity, use "more than" rather than "over," and use "fewer than" or "less than" rather than "under." In cases involving temperature, use "higher than" or "lower than" or "warmer than" or "cooler than." In cases involving weight, use "heavier than" or "lighter than."
parallelism
Use parallel construction in sentences as well as in lists. Express all similar sentence elements (subjects, verbs, verbals, objects) in a similar way.
The lever was moved completely forward, going slightly to the right, and then it went backward halfway in order to complete the procedure.
We are not only responsible to our chief customer but also the taxpayers.
To complete the procedure, push the lever all the way forward, slide it slightly to the right, and then pull it halfway back.
We are responsible not only to our chief customer but also to the taxpayers.
personal pronouns
First-person pronouns may be used in technical communications when appropriate, and some scientific and technical associations (such as the American Institute of Physics) encourage technical writers to do so. Common first-person pronouns include "we," "our," and "us." Personal pronouns can prevent confusion by clearly and concisely showing who performed an experiment or procedure.
We deposited a thin film of doped cadmium on the substrate.
Which of the following two sentences is easier to read and understand quickly?
We agreed that the workshop was a success.
See also active voice and passive voice.
prefixes
See hyphens, compound words, and unit modifiers and scientific notation.
principal and principle
"Principal" often means "chief" or "main," such as the principal investigator in a research project or the principal of a high school. "Principle" often refers to a belief, value, or rule.
race and ethnicity
As a laboratory that strives for diversity of perspectives and inclusivity, our word choices, style, and tone must be carefully considered, particularly when it comes to topics related to race and ethnicity.
Capitalize Black when referring to African Americans or, more broadly, in any racial, ethnic, or cultural sense; do not capitalize white. Do not use the terms “Black(s)” or “white(s)” as singular or stand-alone nouns referring to a person or people. In the plural form, “Black people,” “white people,” “Black scientists,” and “white scientists” are preferable when clearly relevant.
Capitalize “Indigenous” in reference to original inhabitants of a place, aligning with long-standing capitalization of other racial and ethnic identifiers such as Latino, Asian American, and Native American. (Note that no hyphen is used in dual heritage terms such as “Asian American” and “Mexican American.”) Capitalize “Elder” when referring to a Tribal or religious leader, but lowercase it when used to identify someone by age or when used generally.
The terms “Tribal” and “Tribe” should be capitalized, even when they are not part of an entity’s official name. Capitalize the word “nation” when part of a formal name.
a citizen of the Navajo Nation
NREL researchers invited input from many Tribal councils.
In Alaska, the Indigenous groups are collectively known as Alaska Natives. Both “American Indians” and “Native Americans” are acceptable terms when referring to two or more people of different Tribal affiliations. “First Nation” is the preferred term for native Tribes in Canada. “Indian” is used to describe the peoples and cultures of the South Asian nation of India and should not be used as shorthand for American Indians, unless that is how a particular group prefers to be referenced.
For additional details, refer to the AP Stylebook's race-related coverage.
restrictive phrases and clauses
Do not use commas around restrictive phrases and clauses. They are essential to the meaning of the sentence, in contrast to nonrestrictive phrases and clauses, which simply add information that is not essential.
See also which and that.
spelling
If you can't find a word or phrase in this style guide, consult the following reference guides in this order: (1) The Associated Press Stylebook and (2) Merriam-Webster's Collegiate Dictionary, Eleventh Edition.
For spelling out numbers, see numbers.
that and which
See which and that.
time
Use lowercase a.m. and p.m. (with periods) to denote "ante meridiem" and "post meridiem" (before and after noon). Use a colon to separate hours from minutes except for the top of the hour.
- 11 a.m. (not 11:00 a.m.)
- 3:30 p.m.
unit modifiers
See hyphens, compound words, and unit modifiers.
which and that
Standard American English uses "which" for nonrestrictive or nondefining phrases and clauses and "that" for restrictive or defining phrases and clauses. The word "which" usually signals the approach of added, nonessential information. When a phrase or clause is not essential to the meaning of a sentence, use the relative pronoun "which" and enclose the phrase or clause in commas. See also nonrestrictive phrases and clauses and restrictive phrases and clauses.
When a phrase or clause is essential to the meaning of a sentence (that is, the sentence would not make much sense without it), use "that" and leave out the commas.
Share

